Press Release
Open Net Welcomes the National Human Rights Commission’s Issuance of Policy Recommendations on Online Temporary Measures
Policy-Recommendations-NHRCDownload *An English translation is currently unavailable for this...
Open Net Successfully Defends Nonprofit Employee From Criminal Charges for Using a Free Font
Open-NetDownload *An English translation is currently unavailable for this publication. You can...
Female Cyber Security Expert Training Program Course Registration: 2023 Human Resource Training Course in the Cyber Security Field – 1st Round of Online Course Registration
WISET and Microsoft Korea are hosting the 2023 cyber security expert training course for females...
The Yoon Administration’s Censorship Practices Reminds Us of the 2017 Candlelight Vigils
President Yoon and the members of both the ruling and opposition parties are actively seeking to...

The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace Publishes Report on “Data Governance, Asian Alternatives: How India and Korea are Creating New Models and Policies”.
The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace published a report on data governance in South...
LITIGATION
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
OPEN SEMINAR
Open Net Essay and Video Contest 2016
Please read the Korean original here.
[Open Net Forum] The Miracle at Marrakesh: Doing Justice for the Blind and Visually Impaired While Changing the Culture of Norm Setting at WIPO
Please read the Korean original here.
[Open Net Forum] Era of Big Data and IoT – Is De-identified Information Personal Information?
Please read the Korean original here.
Open Net Holds Seminar on the Copyright Trolls Prevention Bill at the National Assembly
Please read the Korean original here.
[Open Net Fourm] Peer Production of Culture and Knowledge: P2P Technology and Digital Democracy
We know people who are dreaming of and trying to realize a society working on open knowledge and...
COURT ACTIONS
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
education
Protected: Southeast Asian CSOs meet with Google at Summit for Democracy 2024
Password Protected
To view this protected post, enter the password below:
IGF 2023 Kyoto: Consumer Data Rights from Japan to the World
Open Net participated in a workshop titled “Consumer Data Rights from Japan to the World” on...
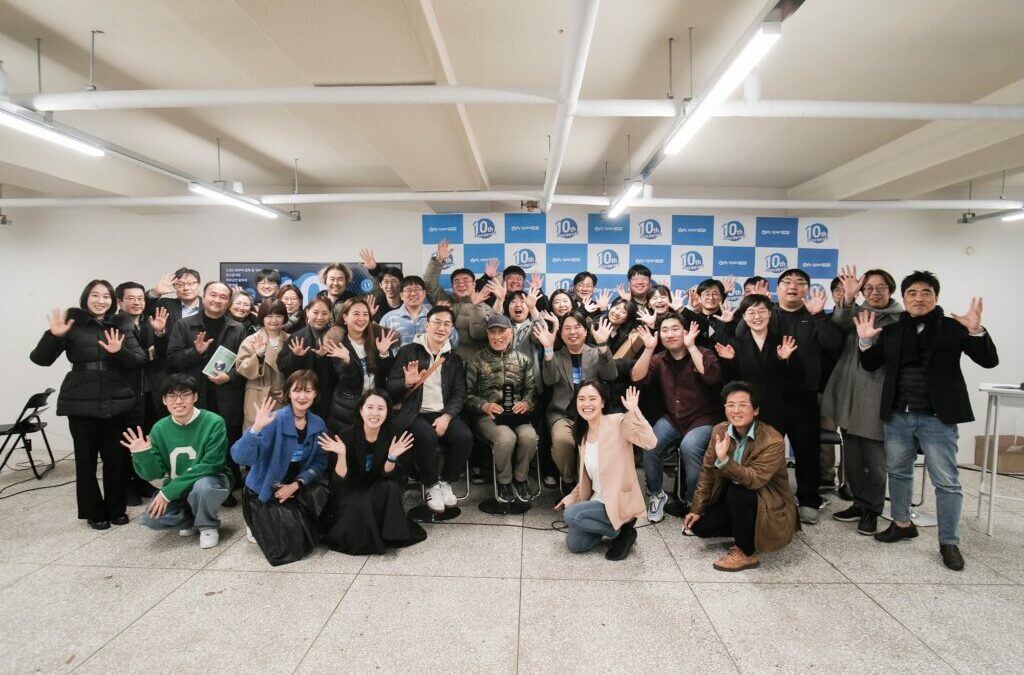

Open Net Celebrated 10th Anniversary on March 8th
On March 8, 2024, Open Net marked its 10th anniversary with a celebration held at the Korea...
Crime of Leaking Classified Information and International Human Rights
by Kyung Sin Park (Open Net Korea Executive Director / Prof. of Korea University Law School...
[Press Release] Condemning KBS President Park Min and KBS PD Lee Je-won Attempting cancellation of a Documentary on the 10th Anniversary of the Sewol Ferry Disaster
February 19, 2024 KBS, the public broadcaster, is regressing to the dark days of the Korean...
POLICY RESEARCH
No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
CAMPAIGN
Stop Internet Censoring
We have seen many attempts to censor the Internet under the pretext of copyright protection. Notorious attempts are SOPA and PIPA of 2012, which triggered the largest online protest in history and was eventually withdrawn, and ACTA, a plurilateral trade deal killed by the European Parliament in 2012. Now, Korean government tries to enact a much stronger internet censoring rule. If it passes the legislative body, a copyright protection agency may cut off access to websites that the agency views as copyright infringing. The concerns over mass surveillance and privacy vulnerabilities by the proposed rule are widespread amid the government’s new drive to block “https” traffic by SNI eavesdropping (See, press release of Korea Communication Commission on February 12, 2019 and press release of MCST on May 2, 2018, both in Korean).
Intermediary Liability Campaign
Korean law (Copyright Act Article 103, Information Communication Network Act Article 44-2) requires intermediaries to take down all content for which anyone sends a takedown notice, regardless whether the content violates any right or law, not as a condition of qualifying for a safe harbor but as a positive obligation. As a result of this ‘mandatory’ notice-and-takedown system, the intermediaries are forced to take down thousands of contents daily which they believe to be perfectly lawful. Also, Korean laws require some intermediaries like P2P and cyberlockers to implement ‘technical measures’ to filter out copyright infringing material (Copyright Act, Article 104) and obscenity (Telecommunications Business Act Article 22-3 Paragraph 1), and requires all intermediaries to implement technical measures to filter out child pornography (Children and Juvenile Sex Protection Act Article 17). These ‘technical measures’ requirement ends up requiring the intermediaries to monitor each and every third party content posted on their services, turning the Internet into a space open to only those contents implicitly permitted by the intermediaries.
Open Net Korea has engaged in various efforts to bring the Korean law into compliance with the international norm, including but not limited to participating in the Steering Committee of the Manila Principles for Intermediary Liability, co-authoring a Good Practice Guideline for Intermediary Liability Regime published by the Network of Centers for Internet and Society, and calling the international community to write to the relevant officials.
Open Payment Campaign
Currently, the law requires all online payments above 300K Korean won (about US$300) to be signed by so-called “accredited certificates”, which are backed only by a Korean government agency operating as a root CA but none of the internationally recognized certificate accreditation agencies and therefore require various plugins to be downloaded from various vendors (most often through Active X technology due to the 90% plus dominance of Internet Explorer in the country) enabling and protecting the certificates. Such monolithic “closed” payment rule made the Korea-based e-commerce inaccessible for overseas customers and very inconvenient for domestic customers and indoctrinated Korean customers into a dangerous habit of accepting downloads of unknown origins, who therefore became easy targets for pfishing and other financial frauds. Open Net calls for the dismantling of the payment rule mandating use of the government-backed-certificates that are not really “accredited” in any global sense.
In 2013, Open Net ran a petition drive to file a Citizens’ Audit on the Korean Financial Services Commission responsible for implementing the closed payment rule, and obtained the sponsorship of more than 300 signatories who signed on-line at this site.
In 2013, Open Net ran a grassroots petition drive here to demand that the authorities overhaul the online payment rule so that the Korean net users can make payments without the nail-biting, computer-freezing, caution-numbing downloading of all the plugins. Several thousands have signed on putting pressure on the legislators and authorities.
In the latter half of 2013, Open Net lobbied for a Digital Signature Act amendment bill allowing digital signatures to be approved by internationally recognized root authorities and a Electronic Financial Transactions Act amendment bill requiring the Financial Services Commission rule-making to be technology-neutral in accordance with the Basel Principles. Here is the campaign headquarter page from which people will gather information and write mails, Twits, FB entries alerting the relevant lawmakers.
“Real” Child Abuse Prevention Campaign
The law punishes virtual images of imaginary children such as in animation and adult-actor films under the same legal scheme as child pornography made of video-recording or “morphing” of real children, which carry mandatory minimum sentence of 5 years for production and, among other things, 10 years of employment ban and 20 years of residential address tracking, not to mention the stigma of “child sex offenders”. Such law resulted in police actions focused on online uploading and downloading of files at the expense of depleted resources for pornography involving real children, which ironically ended up indictment of juvenile computer users as “child sex offenders”. Open Net calls for amendment of the Child and Juvenile Sexual Abuse Prevention Act to make the law serve its real purpose.
Campaign to Strike Out the Three Strikes Rule
In Korea, the copyright Three-Strikes-Out Rule came into effect on July 23, 2009 and gave the government a power to disconnect users from the Internet in the name of copyright protection. So far, although no one has been disconnected from the Internet, 408 website accounts have been shut down and 468,446 warnings or takedowns have been executed by the South Korean government (The Ministry of Culture and the Korean Copyright Commission, an entity empowered to do so without judicial scrutiny under the three-strikes rule). There is no prior judical scrutiny. The government has the full discretion in determining whether the postings or the user accounts are to be taken down or not. This is administrative censorship done fast and cheap for the rightholders, however, suppressing freedom of expression and communication and Internet users’ fundamental right to access, and endangering the future of the free and open Internet.